Engineering Product Development
Engineering product development is the process of designing, developing, and testing a new product or improving an existing one.
This process typically involves a team of engineers, designers and project managers working together to take a product from an initial idea to final production.
The process may include research and analysis, prototyping, testing and validation, design optimization and final production. Engineering product development aims to create a product that meets customer needs and is technically feasible, reliable, and cost-effective to produce.
Product Development Process
The product development process typically consists of the following seven stages:
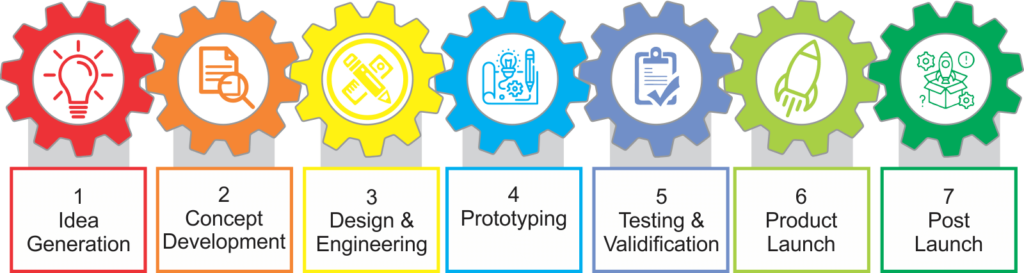
1. Idea Generation
The first step is developing new product ideas. Developing new product ideas can be an exciting but challenging process. Here are some steps you can take to generate and develop new product ideas:
- Brainstorm ideas: Use brainstorming techniques to generate a list of potential product ideas. Encourage creativity, and don’t judge ideas too harshly at this stage.
- Conduct market research: Identify your target market and gather data on their needs and preferences. This information will help you understand what product features and benefits are essential to them.
- Customer Feedback: Customer feedback is essential in engineering product development. It helps to ensure that the final product meets the needs of your target market. There are many ways to gather customer feedback, including surveys, focus groups, social media monitoring, and direct customer interviews. Listening to customer feedback and making improvements based on that feedback can help you create a better final product and build a loyal customer base.
2. Concept Development
Once there are several ideas, the next step is to evaluate and refine them. The refinement process involves turning the idea into a concept and determining its potential marketability.
- Evaluate and refine: Once you have a list of ideas, evaluate them based on factors such as:
- Feasibility,
- Cost, and
- Potential customer demand.
- Narrow down your list and refine your concepts until you have a clear idea of your product.
- Evaluate and refine: Once you have a list of ideas, evaluate them based on factors such as:

3. Design and Engineering
The product is designed and engineered at this stage. Here, the design team will consider the product’s functional requirements, aesthetics and manufacturability.
Create a detailed design, including materials, dimensions, and manufacturing requirements.
The design engineers are responsible for creating and developing new products or systems. They use math and science principles to develop solutions to problems and create designs that meet customer needs and are cost-effective to manufacture.
Design engineers typically work as part of a team and collaborate with other departments such as research and development, marketing, manufacturing, and quality assurance to ensure that their designs are technically feasible, reliable and meet customer needs.
Their responsibilities often include:
- Identifying and defining the problem or need the product or system will address.
- They conduct research and analyze data to develop a design solution.
- They create designs using computer-aided design (CAD) software and other tools.
- They test and modify prototypes to ensure they meet customer needs and engineering specifications.
- They collaborate with other departments to ensure the design meets regulatory and safety requirements.
- They develop and maintain design documentation and specifications.
Overall, the goal of a design engineer is to create practical and effective solutions to meet customer needs and bring new products to the market.
4. Prototyping
A working prototype is created after the design is complete. The prototype helps to test and refine the product and identify any issues or areas for improvement.
Prototyping is an essential step in product development, as it allows you to test your ideas and make improvements before moving on to production. Here are some steps to follow to prototype a new product:
- Define your requirements: Start by defining the requirements for your product, such as its size, weight, features, and functionality. Knowing this will help you create a prototype that accurately represents the final product.
- Choose a prototyping method: There are many prototyping methods to choose from, such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection moulding. Choose the method that works best for your product and budget.
- Create a basic prototype: Start by creating a basic prototype that represents the key features of your product. The prototype could be a rough sketch, a cardboard model, or a simple 3D-printed version.

5. Testing and Validation
The prototype is tested and validated to ensure it meets the functional requirements and is reliable and safe.
- Test and refine: Once you have a basic prototype, start testing it to identify any issues or areas for improvement. Use this feedback to refine your prototype until you are satisfied with its performance.
- Create a final prototype: Once you have refined your prototype, create a final version that is as close to the final product as possible. The final prototype will help you identify any last-minute issues before moving on to production.
Remember, prototyping is an iterative process that involves testing and refining your ideas until you have a product that meets your requirements and is ready for production.
6. Product Launch
The final product is launched, marketed and sold to the target audience.
Marketing a new product can be a challenging task. Here are some steps you can follow to market your new product effectively:
- Identify your target audience: Determine who your product is meant for and what their needs are. Knowing the target audience will help you create targeted marketing messages.
- Develop a marketing plan: Create a marketing plan that outlines your goals, strategies, tactics, and budget.
- Build a strong brand: Develop a strong brand identity that resonates with your target audience.
- Leverage social media: Use social media to create buzz around your product launch and engage with your target audience.
- Use influencers: Partner with influencers who can help promote your product to their followers.
- Offer deals and promotions: Offer deals and promotions to encourage people to try your product.
- Gather customer reviews: Encourage customers to leave reviews of your product online to help increase social proof and credibility.
- Attend trade shows: Attend trade shows and events to showcase your product and network with potential customers.
Remember, effective product marketing is an ongoing process that requires constant attention and adjustments. By staying engaged with your target audience and listening to feedback, you can continue to refine your marketing strategies and successfully promote your new product.

7. Post Launch
Finally, the product is monitored and evaluated for performance and customer feedback. Any necessary improvements are made, and the cycle starts again.
After the launch of a product, there are several vital steps to take:
- Monitor feedback: Listen to customer feedback to identify any issues or areas of improvement that need to be addressed.
- Analyze sales data: Review sales data to determine how well the product is selling and whether any adjustments need to be made to the pricing or promotional strategy.
- Provide support: Offer ongoing customer support to help users get the most out of the product and address any issues they may experience.
- Adjust marketing strategies: Use the feedback and sales data to refine your marketing strategies and continue promoting the product to reach new customers.
- Plan for updates: Consider developing updates or new product versions to keep it relevant and meet changing customer needs.
By taking these steps, you can ensure that your product remains successful and continues to meet the needs of your target audience.
Throughout the process, it’s essential to communicate with your team and any external partners or vendors to make sure everyone is on the same page. Additionally, it’s vital to ensure that your product meets any regulatory or safety standards necessary for your industry.

